資訊專欄INFORMATION COLUMN

單眼三維成像是依據多帶帶監控攝像頭健身運動仿真模擬雙目視覺獲得物件和空間里的三維視覺信息內容,下面本文關鍵為大家介紹了對于如何依據python完成單眼三維成像的資料,原文中依據案例編碼推薦的十分詳盡,必須的小伙伴可以借鑒一下
一、單眼三維成像簡述
客觀現實的物件是三維立體的,而我用監控攝像頭獲得的圖象是二維動畫的,但我們可以依據二維圖像認知總體目標三維信息內容。三維重建技術要以相對應的形式解決圖象從而獲得電子計算機可以識別三維立體信息內容,從而對于目標展開分析。而單眼三維成像乃是依據多帶帶監控攝像頭健身運動來仿真模擬雙目視覺,從而得到物件和空間里的三維視覺信息內容,在其中,單眼是指多帶帶監控攝像頭。
二、完成全過程
對其物件開展單眼三維成像的過程當中,有關軟件環境如下所示:
matplotlib3.3.4
numpy1.19.5
opencv-contrib-python3.4.2.16
opencv-python3.4.2.16
pillow8.2.0
python3.6.2
其復建主要包括下列流程:
(1)鏡頭的校準
def camera_calibration(ImagePath):
#循環中斷
criteria=(cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS+cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,30,0.001)
#棋盤格尺寸(棋盤格的交叉點的個數)
row=11
column=8
objpoint=np.zeros((row*column,3),np.float32)
objpoint[:,:2]=np.mgrid[0:row,0:column].T.reshape(-1,2)
objpoints=[]#3d point in real world space
imgpoints=[]#2d points in image plane.
batch_images=glob.glob(ImagePath+'/*.jpg')
for i,fname in enumerate(batch_images):
img=cv2.imread(batch_images<i>)
imgGray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#find chess board corners
ret,corners=cv2.findChessboardCorners(imgGray,(row,column),None)
#if found,add object points,image points(after refining them)
if ret:
objpoints.append(objpoint)
corners2=cv2.cornerSubPix(imgGray,corners,(11,11),(-1,-1),criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners2)
#Draw and display the corners
img=cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img,(row,column),corners2,ret)
cv2.imwrite('Checkerboard_Image/Temp_JPG/Temp_'+str(i)+'.jpg',img)
print("成功提取:",len(batch_images),"張圖片角點!")
ret,mtx,dist,rvecs,tvecs=cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints,imgpoints,imgGray.shape[::-1],None,None)
(2)圖象圖像匹配及配對
def epipolar_geometric(Images_Path,K):
IMG=glob.glob(Images_Path)
img1,img2=cv2.imread(IMG[0]),cv2.imread(IMG[1])
img1_gray=cv2.cvtColor(img1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2_gray=cv2.cvtColor(img2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#Initiate SURF detector
SURF=cv2.xfeatures2d_SURF.create()
#compute keypoint&descriptions
keypoint1,descriptor1=SURF.detectAndCompute(img1_gray,None)
keypoint2,descriptor2=SURF.detectAndCompute(img2_gray,None)
print("角點數量:",len(keypoint1),len(keypoint2))
#Find point matches
bf=cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2,crossCheck=True)
matches=bf.match(descriptor1,descriptor2)
print("匹配點數量:",len(matches))
src_pts=np.asarray([keypoint1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches])
dst_pts=np.asarray([keypoint2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches])
#plot
knn_image=cv2.drawMatches(img1_gray,keypoint1,img2_gray,keypoint2,matches[:-1],None,flags=2)
image_=Image.fromarray(np.uint8(knn_image))
image_.save("MatchesImage.jpg")
#Constrain matches to fit homography
retval,mask=cv2.findHomography(src_pts,dst_pts,cv2.RANSAC,100.0)
#We select only inlier points
points1=src_pts[mask.ravel()==1]
points2=dst_pts[mask.ravel()==1]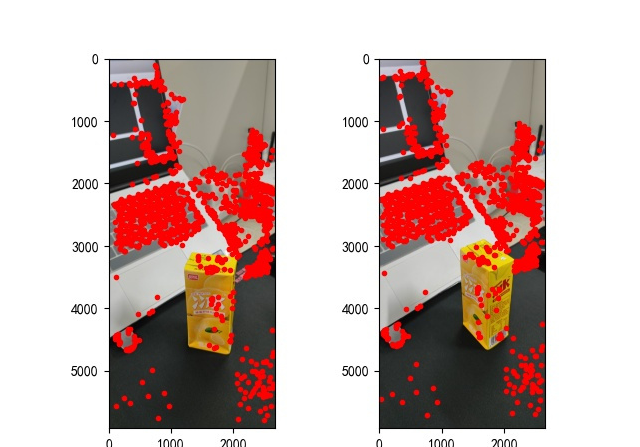
(3)三維成像
points1=cart2hom(points1.T)
points2=cart2hom(points2.T)
#plot
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,2)
ax[0].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[0].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[0].plot(points1[0],points1[1],'r.')
ax[1].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[1].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[1].plot(points2[0],points2[1],'r.')
plt.savefig('MatchesPoints.jpg')
fig.show()
#
points1n=np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K),points1)
points2n=np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K),points2)
E=compute_essential_normalized(points1n,points2n)
print('Computed essential matrix:',(-E/E[0][1]))
P1=np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0]])
P2s=compute_P_from_essential(E)
ind=-1
for i,P2 in enumerate(P2s):
#Find the correct camera parameters
d1=reconstruct_one_point(points1n[:,0],points2n[:,0],P1,P2)
#Convert P2 from camera view to world view
P2_homogenous=np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2,[0,0,0,1]]))
d2=np.dot(P2_homogenous[:3,:4],d1)
if d1[2]>0 and d2[2]>0:
ind=i
P2=np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2s[ind],[0,0,0,1]]))[:3,:4]
Points3D=linear_triangulation(points1n,points2n,P1,P2)
fig=plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('3D reconstructed',fontsize=16)
ax=fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot(Points3D[0],Points3D[1],Points3D[2],'b.')
ax.set_xlabel('x axis')
ax.set_ylabel('y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('z axis')
ax.view_init(elev=135,azim=90)
plt.savefig('Reconstruction.jpg')
plt.show()下面,我們一起來詳盡看看每個流程的實際完成:
(1)鏡頭的校準
在咱們在日常生活中有許多照相機,如手機上面的照相機、數碼照相機及程序模塊型照相機這些,每個鏡頭的主要參數都是不一樣的,即照相機拍出來的手機照片屏幕分辨率、方式等。假定大家在開展物件三維成像時,事前并不了解大家鏡頭的引流矩陣主要參數,那樣,大家就應該算出鏡頭的引流矩陣主要參數,這個流程就叫鏡頭的校準。相機標定的有關基本原理我不講了,在網上許多人講的挺詳盡的。其校準的實際完成如下所示:
在其中,cv2.calibrateCamera函數公式求出來的mtx引流矩陣即是K引流矩陣。
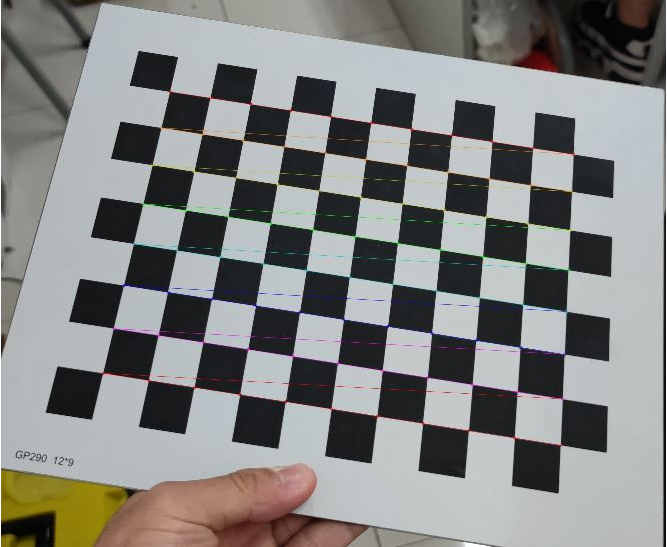
當改動好相對應主要參數并進行校準后,我們能導出棋盤格的角點照片來看看是不是已正式獲取棋盤格的角點,導出角點圖如下所示:
圖1:棋盤格角點獲取
(2)圖象圖像匹配及配對
在所有三維成像的過程當中,這步是相當重要的,也是比較繁雜的一歩,照片圖像匹配的好與壞決定你最后復建實際效果。
在照片特征點獲取優化算法中,主要有三種優化算法比較常見,分別是:SIFT優化算法、SURF優化算法及其ORB優化算法。依據全面分析比照,大家在這里一歩中選用SURF優化算法的方式對圖形的特征點開展獲取。3種算法的特征點獲取實際效果比照如果你們有興趣能去網上搜索來看一下,在這個也不逐個考察了。實際完成如下所示:
圖2:特征點獲取
(3)三維成像
大家尋找圖形的特征點并彼此配對后,則可開始啟動三維成像了,實際完成如下所示:
圖3:三維成像
三、結果
從復建得到的結果來說,單眼三維成像實際效果通常,我覺得可能和這幾個方面有一定關系:
(1)圖片拍攝方式。假如是開展單眼三維成像每日任務,在拍攝圖片的時候最好維持平行移動照相機,且最好是正面拍攝,即不必橫著拍或特殊視角照相;
(2)拍攝的時候周圍環境影響。選擇拍的地址最好是維持單一化,降低不相干一個物體影響;
(3)照相燈源難題。選擇的照相場所要確保適宜的色度(詳細情況要試才發現你的燈源是不是合格),另外就是挪動照相機的時候一定要確保上一時時刻刻和此階段的燈源統一性。
實際上,單眼三維成像效果的確通常,即使將各個方面情形都打滿,很有可能所得到的復建效果也是并不是很好。或是大家可以選擇選用雙眼三維成像,雙眼三維成像實際效果肯定要比單目地比較好的,在推進是可能就不便一(億)一點,嘿嘿。其實并沒有多不少實際操作,主要是整2個相機拍攝和校準2個照相機不便點,其它的都不重要了。
四、編碼
此次試驗的所有編碼如下所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/DeepVegChicken/Learning-3DReconstruction
import cv2
import json
import numpy as np
import glob
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
def cart2hom(arr):
"""Convert catesian to homogenous points by appending a row of 1s
:param arr:array of shape(num_dimension x num_points)
:returns:array of shape((num_dimension+1)x num_points)
"""
if arr.ndim==1:
return np.hstack([arr,1])
return np.asarray(np.vstack([arr,np.ones(arr.shape[1])]))
def compute_P_from_essential(E):
"""Compute the second camera matrix(assuming P1=[I 0])
from an essential matrix.E=[t]R
:returns:list of 4 possible camera matrices.
"""
U,S,V=np.linalg.svd(E)
#Ensure rotation matrix are right-handed with positive determinant
if np.linalg.det(np.dot(U,V))<0:
V=-V
#create 4 possible camera matrices(Hartley p 258)
W=np.array([[0,-1,0],[1,0,0],[0,0,1]])
P2s=[np.vstack((np.dot(U,np.dot(W,V)).T,U[:,2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U,np.dot(W,V)).T,-U[:,2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U,np.dot(W.T,V)).T,U[:,2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U,np.dot(W.T,V)).T,-U[:,2])).T]
return P2s
def correspondence_matrix(p1,p2):
p1x,p1y=p1[:2]
p2x,p2y=p2[:2]
return np.array([
p1x*p2x,p1x*p2y,p1x,
p1y*p2x,p1y*p2y,p1y,
p2x,p2y,np.ones(len(p1x))
]).T
return np.array([
p2x*p1x,p2x*p1y,p2x,
p2y*p1x,p2y*p1y,p2y,
p1x,p1y,np.ones(len(p1x))
]).T
def scale_and_translate_points(points):
"""Scale and translate image points so that centroid of the points
are at the origin and avg distance to the origin is equal to sqrt(2).
:param points:array of homogenous point(3 x n)
:returns:array of same input shape and its normalization matrix
"""
x=points[0]
y=points[1]
center=points.mean(axis=1)#mean of each row
cx=x-center[0]#center the points
cy=y-center[1]
dist=np.sqrt(np.power(cx,2)+np.power(cy,2))
scale=np.sqrt(2)/dist.mean()
norm3d=np.array([
[scale,0,-scale*center[0]],
[0,scale,-scale*center[1]],
[0,0,1]
])
return np.dot(norm3d,points),norm3d
def compute_image_to_image_matrix(x1,x2,compute_essential=False):
"""Compute the fundamental or essential matrix from corresponding points
(x1,x2 3*n arrays)using the 8 point algorithm.
Each row in the A matrix below is constructed as
[x'*x,x'*y,x',y'*x,y'*y,y',x,y,1]
"""
A=correspondence_matrix(x1,x2)
#compute linear least square solution
U,S,V=np.linalg.svd(A)
F=V[-1].reshape(3,3)
#constrain F.Make rank 2 by zeroing out last singular value
U,S,V=np.linalg.svd(F)
S[-1]=0
if compute_essential:
S=[1,1,0]#Force rank 2 and equal eigenvalues
F=np.dot(U,np.dot(np.diag(S),V))
return F
def compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1,p2,compute_essential=False):
"""Computes the fundamental or essential matrix from corresponding points
using the normalized 8 point algorithm.
:input p1,p2:corresponding points with shape 3 x n
:returns:fundamental or essential matrix with shape 3 x 3
"""
n=p1.shape[1]
if p2.shape[1]!=n:
raise ValueError('Number of points do not match.')
#preprocess image coordinates
p1n,T1=scale_and_translate_points(p1)
p2n,T2=scale_and_translate_points(p2)
#compute F or E with the coordinates
F=compute_image_to_image_matrix(p1n,p2n,compute_essential)
#reverse preprocessing of coordinates
#We know that P1'E P2=0
F=np.dot(T1.T,np.dot(F,T2))
return F/F[2,2]
def compute_fundamental_normalized(p1,p2):
return compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1,p2)
def compute_essential_normalized(p1,p2):
return compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1,p2,compute_essential=True)
def skew(x):
"""Create a skew symmetric matrix*A*from a 3d vector*x*.
Property:np.cross(A,v)==np.dot(x,v)
:param x:3d vector
:returns:3 x 3 skew symmetric matrix from*x*
"""
return np.array([
[0,-x[2],x[1]],
[x[2],0,-x[0]],
[-x[1],x[0],0]
])
def reconstruct_one_point(pt1,pt2,m1,m2):
"""
pt1 and m1*X are parallel and cross product=0
pt1 x m1*X=pt2 x m2*X=0
"""
A=np.vstack([
np.dot(skew(pt1),m1),
np.dot(skew(pt2),m2)
])
U,S,V=np.linalg.svd(A)
P=np.ravel(V[-1,:4])
return P/P[3]
def linear_triangulation(p1,p2,m1,m2):
"""
Linear triangulation(Hartley ch 12.2 pg 312)to find the 3D point X
where p1=m1*X and p2=m2*X.Solve AX=0.
:param p1,p2:2D points in homo.or catesian coordinates.Shape(3 x n)
:param m1,m2:Camera matrices associated with p1 and p2.Shape(3 x 4)
:returns:4 x n homogenous 3d triangulated points
"""
num_points=p1.shape[1]
res=np.ones((4,num_points))
for i in range(num_points):
A=np.asarray([
(p1[0,i]*m1[2,:]-m1[0,:]),
(p1[1,i]*m1[2,:]-m1[1,:]),
(p2[0,i]*m2[2,:]-m2[0,:]),
(p2[1,i]*m2[2,:]-m2[1,:])
])
_,_,V=np.linalg.svd(A)
X=V[-1,:4]
res[:,i]=X/X[3]
return res
def writetofile(dict,path):
for index,item in enumerate(dict):
dict[item]=np.array(dict[item])
dict[item]=dict[item].tolist()
js=json.dumps(dict)
with open(path,'w')as f:
f.write(js)
print("參數已成功保存到文件")
def readfromfile(path):
with open(path,'r')as f:
js=f.read()
mydict=json.loads(js)
print("參數讀取成功")
return mydict
def camera_calibration(SaveParamPath,ImagePath):
#循環中斷
criteria=(cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS+cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,30,0.001)
#棋盤格尺寸
row=11
column=8
objpoint=np.zeros((row*column,3),np.float32)
objpoint[:,:2]=np.mgrid[0:row,0:column].T.reshape(-1,2)
objpoints=[]#3d point in real world space
imgpoints=[]#2d points in image plane.
batch_images=glob.glob(ImagePath+'/*.jpg')
for i,fname in enumerate(batch_images):
img=cv2.imread(batch_images<i>)
imgGray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#find chess board corners
ret,corners=cv2.findChessboardCorners(imgGray,(row,column),None)
#if found,add object points,image points(after refining them)
if ret:
objpoints.append(objpoint)
corners2=cv2.cornerSubPix(imgGray,corners,(11,11),(-1,-1),criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners2)
#Draw and display the corners
img=cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img,(row,column),corners2,ret)
cv2.imwrite('Checkerboard_Image/Temp_JPG/Temp_'+str(i)+'.jpg',img)
print("成功提取:",len(batch_images),"張圖片角點!")
ret,mtx,dist,rvecs,tvecs=cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints,imgpoints,imgGray.shape[::-1],None,None)
dict={'ret':ret,'mtx':mtx,'dist':dist,'rvecs':rvecs,'tvecs':tvecs}
writetofile(dict,SaveParamPath)
meanError=0
for i in range(len(objpoints)):
imgpoints2,_=cv2.projectPoints(objpoints<i>,rvecs<i>,tvecs<i>,mtx,dist)
error=cv2.norm(imgpoints<i>,imgpoints2,cv2.NORM_L2)/len(imgpoints2)
meanError+=error
print("total error:",meanError/len(objpoints))
def epipolar_geometric(Images_Path,K):
IMG=glob.glob(Images_Path)
img1,img2=cv2.imread(IMG[0]),cv2.imread(IMG[1])
img1_gray=cv2.cvtColor(img1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2_gray=cv2.cvtColor(img2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#Initiate SURF detector
SURF=cv2.xfeatures2d_SURF.create()
#compute keypoint&descriptions
keypoint1,descriptor1=SURF.detectAndCompute(img1_gray,None)
keypoint2,descriptor2=SURF.detectAndCompute(img2_gray,None)
print("角點數量:",len(keypoint1),len(keypoint2))
#Find point matches
bf=cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2,crossCheck=True)
matches=bf.match(descriptor1,descriptor2)
print("匹配點數量:",len(matches))
src_pts=np.asarray([keypoint1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches])
dst_pts=np.asarray([keypoint2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches])
#plot
knn_image=cv2.drawMatches(img1_gray,keypoint1,img2_gray,keypoint2,matches[:-1],None,flags=2)
image_=Image.fromarray(np.uint8(knn_image))
image_.save("MatchesImage.jpg")
#Constrain matches to fit homography
retval,mask=cv2.findHomography(src_pts,dst_pts,cv2.RANSAC,100.0)
#We select only inlier points
points1=src_pts[mask.ravel()==1]
points2=dst_pts[mask.ravel()==1]
points1=cart2hom(points1.T)
points2=cart2hom(points2.T)
#plot
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,2)
ax[0].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[0].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[0].plot(points1[0],points1[1],'r.')
ax[1].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[1].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[1].plot(points2[0],points2[1],'r.')
plt.savefig('MatchesPoints.jpg')
fig.show()
#
points1n=np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K),points1)
points2n=np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K),points2)
E=compute_essential_normalized(points1n,points2n)
print('Computed essential matrix:',(-E/E[0][1]))
P1=np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0]])
P2s=compute_P_from_essential(E)
ind=-1
for i,P2 in enumerate(P2s):
#Find the correct camera parameters
d1=reconstruct_one_point(points1n[:,0],points2n[:,0],P1,P2)
#Convert P2 from camera view to world view
P2_homogenous=np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2,[0,0,0,1]]))
d2=np.dot(P2_homogenous[:3,:4],d1)
if d1[2]>0 and d2[2]>0:
ind=i
P2=np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2s[ind],[0,0,0,1]]))[:3,:4]
Points3D=linear_triangulation(points1n,points2n,P1,P2)
return Points3D
def main():
CameraParam_Path='CameraParam.txt'
CheckerboardImage_Path='Checkerboard_Image'
Images_Path='SubstitutionCalibration_Image/*.jpg'
#計算相機參數
camera_calibration(CameraParam_Path,CheckerboardImage_Path)
#讀取相機參數
config=readfromfile(CameraParam_Path)
K=np.array(config['mtx'])
#計算3D點
Points3D=epipolar_geometric(Images_Path,K)
#重建3D點
fig=plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('3D reconstructed',fontsize=16)
ax=fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot(Points3D[0],Points3D[1],Points3D[2],'b.')
ax.set_xlabel('x axis')
ax.set_ylabel('y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('z axis')
ax.view_init(elev=135,azim=90)
plt.savefig('Reconstruction.jpg')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()綜上所述,這篇文章就給大家介紹到這里了,希望可以給大家帶來幫助。
文章版權歸作者所有,未經允許請勿轉載,若此文章存在違規行為,您可以聯系管理員刪除。
轉載請注明本文地址:http://specialneedsforspecialkids.com/yun/130254.html
摘要:兩條平行的直線在無窮遠的地方看起來會匯集到一起,而匯集的點,在透視里稱作消失點。小孔成像三維空間的火焰,透過小孔,在二維成像屏上顯示了二維的畫面。 前言 不好意思,標題其實是開了個玩笑。大家都知道,Canvas 獲取繪畫上下文的 api 是 getContext(2d)。我第一次看到這個 api 定義的時候,就很自然的認為,既然有 2d 那一定是有 3d 的咯? 但是我接著我看到了 a...
??歡迎訂閱《從實戰學python》專欄,用python實現爬蟲、辦公自動化、數據可視化、人工智能等各個方向的實戰案例,有趣又有用!?? 更多精品專欄簡介點這里 治愈生活的良方 就是保持對生活的熱愛 前言 哈嘍,大家好,我是一條。 每次和女朋友出去玩,拍照是必須的,天氣好還行,天氣要是不好,加上我這破手機,那拍的簡直慘不忍睹,自己都不過去。 但是沒什么能難倒程序員的,為了不挨罵,連夜寫出去霧...
contour和contourf全是畫三維立體等高線圖的,接下來本文主要是為大家介紹了關于python做圖基本操作之plt.contour的相關信息,原文中依據案例編碼推薦的十分詳盡,需用的小伙伴可以參考一下 序言 plt.contour是python中用以畫等值線的函數公式,這兒簡單的介紹plt.contour的應用。 應用示例 importnumpyasnp importmat...
摘要:在文末,我會附上一個可加載的模型方便學習中文藝術字渲染用原生可以很容易地繪制文字,但是原生提供的文字效果美化功能十分有限。 showImg(https://segmentfault.com/img/bVWYnb?w=900&h=385); WebGL 可以說是 HTML5 技術生態鏈中最為令人振奮的標準之一,它把 Web 帶入了 3D 的時代。 初識 WebGL 先通過幾個使用 Web...
閱讀 910·2023-01-14 11:38
閱讀 877·2023-01-14 11:04
閱讀 739·2023-01-14 10:48
閱讀 1980·2023-01-14 10:34
閱讀 941·2023-01-14 10:24
閱讀 818·2023-01-14 10:18
閱讀 498·2023-01-14 10:09
閱讀 571·2023-01-14 10:02