資訊專欄INFORMATION COLUMN

小編寫這篇文章的一個主要目的,主要是來給大家去做一個介紹,介紹的內(nèi)容主要是關(guān)于Python的一些知識,其中的內(nèi)容包含有xpath,JsonPath,bs4等一些知識,主要是去介紹他們的一些基本使用方法,具體的內(nèi)容,下面就給大家詳細解答下。
1.xpath
1.1 xpath使用
google提前安裝xpath插件,按ctrl+shift+x出現(xiàn)小黑框
安裝lxml庫pip install lxml‐i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
導入lxml.etreefrom lxml import etree
etree.parse()解析本地文件html_tree=etree.parse('XX.html')
etree.HTML()服務(wù)器響應(yīng)文件html_tree=etree.HTML(response.read().decode('utf‐8')
.html_tree.xpath(xpath路徑)
1.2 xpath基本語法
1.路徑查詢
查找所有子孫節(jié)點,不考慮層級關(guān)系
找直接子節(jié)點
2.謂詞查詢
//div[id] //div[id="maincontent"]
3.屬性查詢
//class
4.模糊查詢
//div[contains(id,"he")] //div[starts‐with(id,"he")]
5.內(nèi)容查詢
//div/h1/text()
6.邏輯運算
//div[id="head"and] //title|//price
1.3示例
xpath.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li id="l1"class="class1">北京</li>
<li id="l2"class="class2">上海</li>
<li id="d1">廣州</li>
<li>深圳</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
from lxml import etree
#xpath解析
#本地文件:etree.parse
#服務(wù)器相應(yīng)的數(shù)據(jù)response.read().decode('utf-8')etree.HTML()
tree=etree.parse('xpath.html')
#查找url下邊的li
li_list=tree.xpath('//body/ul/li')
print(len(li_list))#4
#獲取標簽中的內(nèi)容
li_list=tree.xpath('//body/ul/li/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京','上海','廣州','深圳']
#獲取帶id屬性的li
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id]')
print(len(li_list))#3
#獲取id為l1的標簽內(nèi)容
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l1"]/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京']
#獲取id為l1的class屬性值
c1=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l1"]/class')
print(c1)#['class1']
#獲取id中包含l的標簽
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[contains(id,"l")]/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京','上海']
#獲取id以d開頭的標簽
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[starts-with(id,"d")]/text()')
print(li_list)#['廣州']
#獲取id為l2并且class為class2的標簽
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l2"and]/text()')
print(li_list)#['上海']
#獲取id為l2或id為d1的標簽
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l2"]/text()|//ul/li[id="d1"]/text()')
print(li_list)#['上海','廣州']1.4爬取百度搜索按鈕的value
import urllib.request
from lxml import etree
url='http://www.baidu.com'
headers={
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64)AppleWebKit/537.36(KHTML,like Gecko)Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request=urllib.request.Request(url=url,headers=headers)
response=urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
tree=etree.HTML(content)
value=tree.xpath('//input[id="su"]/value')
print(value)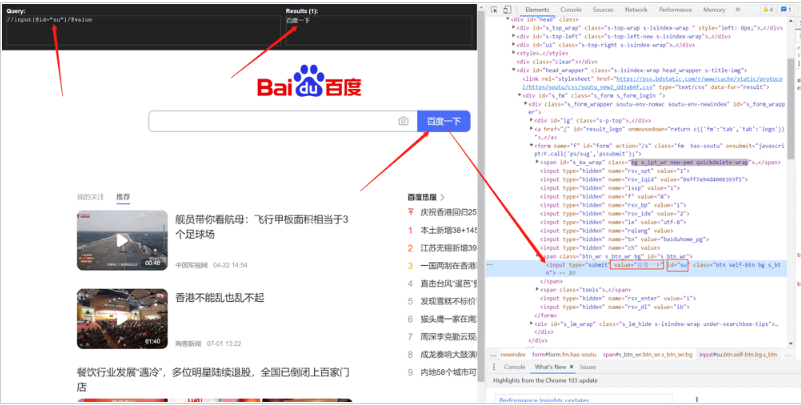
1.5爬取站長素材的圖片
#需求下載的前十頁的圖片
#https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian.html 1
#https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian_page.html
import urllib.request
from lxml import etree
def create_request(page):
if(page==1):
url='https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian.html'
else:
url='https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian_'+str(page)+'.html'
headers={
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64)AppleWebKit/537.36(KHTML,like Gecko)Chrome/92.0.4515.159 Safari/537.36',
}
request=urllib.request.Request(url=url,headers=headers)
return request
def get_content(request):
response=urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
return content
def down_load(content):
#下載圖片
#urllib.request.urlretrieve('圖片地址','文件的名字')
tree=etree.HTML(content)
name_list=tree.xpath('//div[id="container"]//a/img/alt')
#一般設(shè)計圖片的網(wǎng)站都會進行懶加載
src_list=tree.xpath('//div[id="container"]//a/img/src2')
print(src_list)
for i in range(len(name_list)):
name=name_list<i>
src=src_list<i>
url='https:'+src
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=url,filename='./loveImg/'+name+'.jpg')
if __name__=='__main__':
start_page=int(input('請輸入起始頁碼'))
end_page=int(input('請輸入結(jié)束頁碼'))
for page in range(start_page,end_page+1):
#(1)請求對象的定制
request=create_request(page)
#(2)獲取網(wǎng)頁的源碼
content=get_content(request)
#(3)下載
down_load(content)2.JsonPath
2.1 pip安裝
pip install jsonpath
2.2 jsonpath的使用
obj=json.load(open('json文件','r',encoding='utf‐8'))
ret=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'jsonpath語法')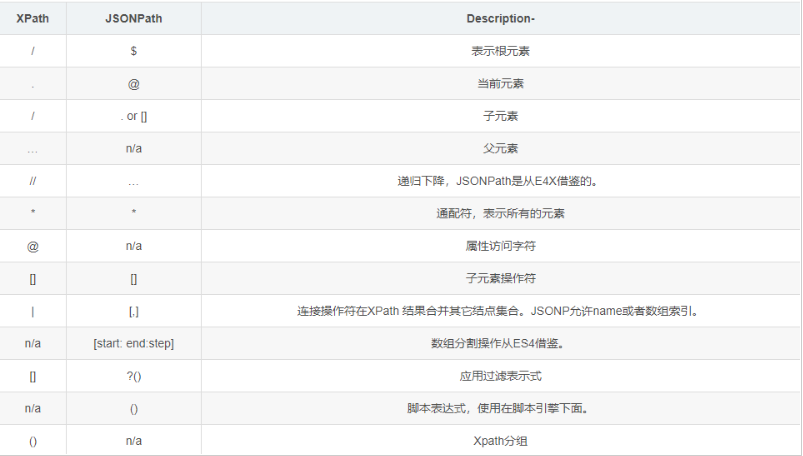
JSONPath語法元素和對應(yīng)XPath元素的對比:
示例:
jsonpath.json
{"store":{
"book":[
{"category":"修真",
"author":"六道",
"title":"壞蛋是怎樣練成的",
"price":8.95
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"天蠶土豆",
"title":"斗破蒼穹",
"price":12.99
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"唐家三少",
"title":"斗羅大陸",
"isbn":"0-553-21311-3",
"price":8.99
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"南派三叔",
"title":"星辰變",
"isbn":"0-395-19395-8",
"price":22.99
}
],
"bicycle":{
"author":"老馬",
"color":"黑色",
"price":19.95
}
}
}
import json
import jsonpath
obj=json.load(open('jsonpath.json','r',encoding='utf-8'))
#書店所有書的作者
author_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store.book[*].author')
print(author_list)#['六道','天蠶土豆','唐家三少','南派三叔']
#所有的作者
author_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..author')
print(author_list)#['六道','天蠶土豆','唐家三少','南派三叔','老馬']
#store下面的所有的元素
tag_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store.*')
print(
tag_list)#[[{'category':'修真','author':'六道','title':'壞蛋是怎樣練成的','price':8.95},{'category':'修真','author':'天蠶土豆','title':'斗破蒼穹','price':12.99},{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗羅大陸','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰變','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}],{'author':'老馬','color':'黑色','price':19.95}]
#store里面所有東西的price
price_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store..price')
print(price_list)#[8.95,12.99,8.99,22.99,19.95]
#第三個書
book=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[2]')
print(book)#[{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗羅大陸','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99}]
#最后一本書
book=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[(.length-1)]')
print(book)#[{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰變','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]
#前面的兩本書
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[0,1]')
#book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[:2]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'六道','title':'壞蛋是怎樣練成的','price':8.95},{'category':'修真','author':'天蠶土豆','title':'斗破蒼穹','price':12.99}]
#條件過濾需要在()的前面添加一個?
#過濾出所有的包含isbn的書。
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[?(.isbn)]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗羅大陸','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰變','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]
#哪本書超過了10塊錢
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[?(.price>10)]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'天蠶土豆','title':'斗破蒼穹','price':12.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰變','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]3.BeautifulSoup
3.1基本簡介
1.安裝
pip install bs4
2.導入
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
3.創(chuàng)建對象
服務(wù)器響應(yīng)的文件生成對象soup=BeautifulSoup(response.read().decode(),'lxml')
本地文件生成對象soup=BeautifulSoup(open('1.html'),'lxml')
注意:默認打開文件的編碼格式gbk所以需要指定打開編碼格式utf-8
3.2安裝以及創(chuàng)建
1.根據(jù)標簽名查找節(jié)點
soup.a【注】只能找到第一個a soup.a.name soup.a.attrs
2.函數(shù)
(1).find(返回一個對象)
find('a'):只找到第一個a標簽
find('a',title='名字')
find('a',class_='名字')
(2).find_all(返回一個列表)
find_all('a')查找到所有的a
find_all(['a','span'])返回所有的a和span
find_all('a',limit=2)只找前兩個a
(3).select(根據(jù)選擇器得到節(jié)點對象)【推薦】
1.element
eg:p
2..class
eg:.firstname
3.#id
eg:#firstname
4.屬性選擇器
[attribute]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class]')
[attribute=value]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class="hengheng1"]')
5.層級選擇器
element element
div p
element>element
div>p
element,element
div,p
eg:soup=soup.select('a,span')
3.3節(jié)點定位
1.根據(jù)標簽名查找節(jié)點
soup.a【注】只能找到第一個a
soup.a.name
soup.a.attrs
2.函數(shù)
(1).find(返回一個對象)
find('a'):只找到第一個a標簽
find('a',title='名字')
find('a',class_='名字')
(2).find_all(返回一個列表)
find_all('a')查找到所有的a
find_all(['a','span'])返回所有的a和span
find_all('a',limit=2)只找前兩個a
(3).select(根據(jù)選擇器得到節(jié)點對象)【推薦】
1.element
eg:p
2..class
eg:.firstname
3.#id
eg:#firstname
4.屬性選擇器
[attribute]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class]')
[attribute=value]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class="hengheng1"]')
5.層級選擇器
element element
div p
element>element
div>p
element,element
div,p
eg:soup=soup.select('a,span')
3.5節(jié)點信息
(1).獲取節(jié)點內(nèi)容:適用于標簽中嵌套標簽的結(jié)構(gòu)
obj.string
obj.get_text()【推薦】
(2).節(jié)點的屬性
tag.name獲取標簽名
eg:tag=find('li)
print(tag.name)
tag.attrs將屬性值作為一個字典返回
(3).獲取節(jié)點屬性
obj.attrs.get('title')【常用】
obj.get('title')
obj['title']
(1).獲取節(jié)點內(nèi)容:適用于標簽中嵌套標簽的結(jié)構(gòu)
obj.string
obj.get_text()【推薦】
(2).節(jié)點的屬性
tag.name獲取標簽名
eg:tag=find('li)
print(tag.name)
tag.attrs將屬性值作為一個字典返回
(3).獲取節(jié)點屬性
obj.attrs.get('title')【常用】
obj.get('title')
obj['title']
3.6使用示例
bs4.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li id="l1">張三</li>
<li id="l2">李四</li>
<li>王五</li>
<a href=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow""class="a1">google</a>
<span>嘿嘿嘿</span>
</ul>
</div>
<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>
<div id="d1">
<span>
哈哈哈
</span>
</div>
<p id="p1"class="p1">呵呵呵</p>
</body>
</html>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#通過解析本地文件來將bs4的基礎(chǔ)語法進行講解
#默認打開的文件的編碼格式是gbk所以在打開文件的時候需要指定編碼
soup=BeautifulSoup(open('bs4.html',encoding='utf-8'),'lxml')
#根據(jù)標簽名查找節(jié)點
#找到的是第一個符合條件的數(shù)據(jù)
print(soup.a)#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#獲取標簽的屬性和屬性值
print(soup.a.attrs)#{'href':'','id':'','class':['a1']}
#bs4的一些函數(shù)
#(1)find
#返回的是第一個符合條件的數(shù)據(jù)
print(soup.find('a'))#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#根據(jù)title的值來找到對應(yīng)的標簽對象
print(soup.find('a',title="a2"))#<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>
#根據(jù)class的值來找到對應(yīng)的標簽對象注意的是class需要添加下劃線
print(soup.find('a',class_="a1"))#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#(2)find_all返回的是一個列表并且返回了所有的a標簽
print(soup.find_all('a'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#如果想獲取的是多個標簽的數(shù)據(jù)那么需要在find_all的參數(shù)中添加的是列表的數(shù)據(jù)
print(soup.find_all(['a','span']))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<span>嘿嘿嘿</span>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百</a><spa哈</span>]
#limit的作用是查找前幾個數(shù)據(jù)
print(soup.find_all('li',limit=2))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#(3)select(推薦)
#select方法返回的是一個列表并且會返回多個數(shù)據(jù)
print(soup.select('a'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#可以通過.代表class我們把這種操作叫做類選擇器
print(soup.select('.a1'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>]
print(soup.select('#l1'))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>]
#屬性選擇器---通過屬性來尋找對應(yīng)的標簽
#查找到li標簽中有id的標簽
print(soup.select('li[id]'))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#查找到li標簽中id為l2的標簽
print(soup.select('li[id="l2"]'))#[<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#層級選擇器
#后代選擇器
#找到的是div下面的li
print(soup.select('div li'))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>]
#子代選擇器
#某標簽的第一級子標簽
#注意:很多的計算機編程語言中如果不加空格不會輸出內(nèi)容但是在bs4中不會報錯會顯示內(nèi)容
print(soup.select('div>ul>li'))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>]
#找到a標簽和li標簽的所有的對象
print(soup.select(
'a,li'))#[<li id="l1">張三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>,<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#節(jié)點信息
#獲取節(jié)點內(nèi)容
obj=soup.select('#d1')[0]
#如果標簽對象中只有內(nèi)容那么string和get_text()都可以使用
#如果標簽對象中除了內(nèi)容還有標簽?zāi)敲磗tring就獲取不到數(shù)據(jù)而get_text()是可以獲取數(shù)據(jù)
#我們一般情況下推薦使用get_text()
print(obj.string)#None
print(obj.get_text())#哈哈哈
#節(jié)點的屬性
obj=soup.select('#p1')[0]
#name是標簽的名字
print(obj.name)#p
#將屬性值左右一個字典返回
print(obj.attrs)#{'id':'p1','class':['p1']}
#獲取節(jié)點的屬性
obj=soup.select('#p1')[0]
#
print(obj.attrs.get('class'))#['p1']
print(obj.get('class'))#['p1']
print(obj['class'])#['p1']
3.7解析星巴克產(chǎn)品名稱
import urllib.request
url='https://www.starbucks.com.cn/menu/'
response=urllib.request.urlopen(url)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(content,'lxml')
#//ul[class="grid padded-3 product"]//strong/text()
#一般先用xpath方式通過google插件寫好解析的表達式
name_list=soup.select('ul[class="grid padded-3 product"]strong')
for name in name_list:
print(name.get_text())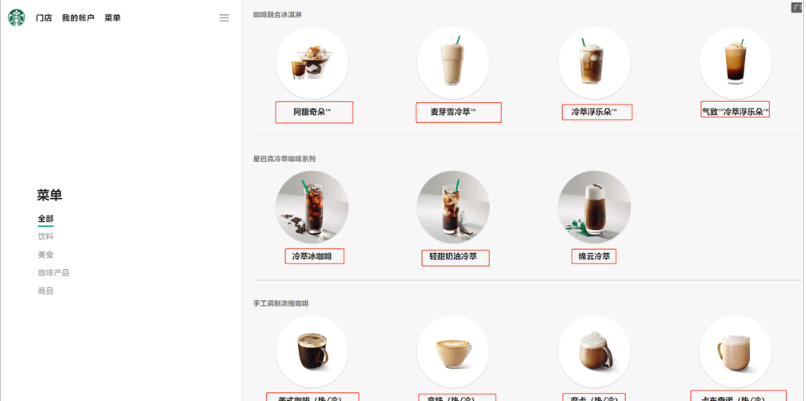
綜上所述,這篇文章就給大家介紹到這里了,希望可以為大家?guī)砀鄮椭?/p>
文章版權(quán)歸作者所有,未經(jīng)允許請勿轉(zhuǎn)載,若此文章存在違規(guī)行為,您可以聯(lián)系管理員刪除。
轉(zhuǎn)載請注明本文地址:http://specialneedsforspecialkids.com/yun/128400.html
摘要:并不是所有爬蟲都遵守,一般只有大型搜索引擎爬蟲才會遵守。的端口號為的端口號為工作原理網(wǎng)絡(luò)爬蟲抓取過程可以理解為模擬瀏覽器操作的過程。表示服務(wù)器成功接收請求并已完成整個處理過程。 爬蟲概念 數(shù)據(jù)獲取的方式: 企業(yè)生產(chǎn)的用戶數(shù)據(jù):大型互聯(lián)網(wǎng)公司有海量用戶,所以他們積累數(shù)據(jù)有天然優(yōu)勢。有數(shù)據(jù)意識的中小型企業(yè),也開始積累的數(shù)據(jù)。 數(shù)據(jù)管理咨詢公司 政府/機構(gòu)提供的公開數(shù)據(jù) 第三方數(shù)據(jù)平臺購買...
摘要:主要用于選擇器抽象類,實現(xiàn)類前面說的兩個接口,主要用于選擇器繼承。多個選擇的情形,每個選擇器各自獨立選擇,將所有結(jié)果合并。抽象類,定義了一些模板方法。這部分源碼就不做分析了。這里需要提到的一點是返回的不支持選擇,返回的對象支持選擇。 1、Selector部分:接口:Selector:定義了根據(jù)字符串選擇單個元素和選擇多個元素的方法。ElementSelector:定義了根據(jù)jsoup ...
摘要:學習爬蟲的背景了解。但是搜索引擎蜘蛛的爬行是被輸入了一定的規(guī)則的,它需要遵從一些命令或文件的內(nèi)容,如標注為的鏈接,或者是協(xié)議。不同領(lǐng)域不同背景的用戶往往具有不同的檢索目的和需求,搜索引擎無法提供針對具體某個用戶的搜索結(jié)果。 學習python爬蟲的背景了解。 大數(shù)據(jù)時代數(shù)據(jù)獲取方式 如今,人類社會已經(jīng)進入了大數(shù)據(jù)時代,數(shù)據(jù)已經(jīng)成為必不可少的部分,可見數(shù)據(jù)的獲取非常重要,而數(shù)據(jù)的獲取的方式...
摘要:大奉打更人賣報小郎君這個人仙太過正經(jīng)言歸正傳從紅月開始黑山老鬼穩(wěn)住別浪跳舞二解析數(shù)據(jù)是一個可以從或文件中提取數(shù)據(jù)的庫。 目錄 一、XPath解析數(shù)據(jù) 1、XPath解析數(shù)據(jù) 2、XML的樹形結(jié)構(gòu) 3、使用XPath選取節(jié)點 4、課堂案例 - 爬取起點小說網(wǎng) 二、BeautifulSoup解析...
閱讀 911·2023-01-14 11:38
閱讀 878·2023-01-14 11:04
閱讀 740·2023-01-14 10:48
閱讀 1982·2023-01-14 10:34
閱讀 942·2023-01-14 10:24
閱讀 819·2023-01-14 10:18
閱讀 499·2023-01-14 10:09
閱讀 572·2023-01-14 10:02